U.S. President Donald Trump says he will enact his long-awaited tariffs on imported vehicles on April 2, defying industry experts who warn that the move will drive up costs for businesses and consumers while undercutting the United States-Mexico-Canada free-trade agreement that he signed in his first term.
Mr. Trump said on Wednesday that automobiles and auto parts imported to the U.S. will face 25-per-cent tariffs. Vehicles imported under the USMCA will be taxed at the same amount based on their non-U.S. content. Auto parts covered by the trade agreement will face tariffs at a later date, also based on their non-U.S. content.
The President has also promised to introduce “reciprocal tariffs” on April 2, which would be an effort to match tariffs and non-tariff barriers that other countries place on U.S. goods.
The automotive tariffs are central to Mr. Trump’s economic nationalist trade policy, which aims to spur domestic manufacturing and persuade foreign companies, especially automakers, to shift production to the U.S. Mr. Trump has said that he wants to “permanently shut down” the Canadian auto industry and annex the country with “economic force.”
The move upends decades of free trade in automobiles between Canada and the U.S., and threatens one of Canada’s key manufacturing sectors. The impact will also be felt by global auto manufacturers that export to the United States.
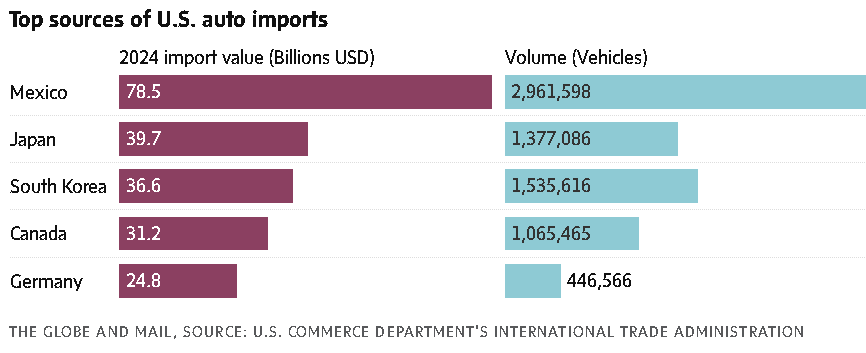
Automakers and parts suppliers employ 125,000 people in this country, mostly in Ontario, and hundreds of thousands more in other businesses. Ontario plants run by Ford, General Motors, Stellantis, Honda and Toyota made a total of 1.6 million passenger vehicles in 2024, according to the Canadian Vehicle Manufacturers’ Association, most of which were exported to the United States.
During a press conference on Wednesday, Mr. Trump said he had spoken with the Detroit-based automakers and said their reaction to the tariffs depended on where they produced their vehicles. “If you have factories here, you’re thrilled,” Mr. Trump said. “If you don’t, you’re going to have to get going and build them, otherwise they have to pay tariffs. It’s very simple.”
The U.S. is relying on Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962 to apply the tariffs on imported cars and car parts, deeming the imports a “threat to national security.”
U.S car sales in 2024 totalled 16 million, half of which were imported, according to a White House statement. Of the 8 million made in the U.S., the average domestic content is as low as 40 per cent, the statement reads. “Therefore, of the 16 million cars bought by Americans, only 25 per cent of the vehicle content can be categorized as Made in America,” the statement said.
Ontario Premier Doug Ford condemned the tariff announcement, which hits his province hard, calling it an “early attack” before the April 2 deadline. He said it would cause the price of cars in the U.S. to rise, while forcing U.S. factories to close as the move disrupts the auto industry’s cross-border supply chains.
President Trump is at it again.
His 25 per cent tariffs on cars and light trucks will do nothing more than increase costs for hard-working American families. U.S. markets are already on the decline as the president causes more chaos and uncertainty. He’s putting American jobs at…— Doug Ford (@fordnation) March 26, 2025
David Adams, president of Global Automakers of Canada, which represents Toyota, Honda and several other manufacturers, said the announcement undercuts Mr. Trump’s campaign promises to tackle affordability and inflation.
“It’s hard to see a good outcome for Canadians or Americans from this announcement,” Mr. Adams said in an interview, predicting that the tariff will reduce Ontario auto production.
“The reality is at some point you’re going to be selling fewer vehicles into the U.S. market, which means that there may have to be production adjustments at some point down the line,” Mr. Adams said. “The longer these tariffs stay in place, the more challenging it becomes for vehicle producers here in Canada.”
Fraser Johnson, a professor at Western University’s Ivey Business School, said the tariffs will have “significant repercussions” for the Canadian automotive industry and the investments the companies make. However, he said car makers will not move their Ontario plants south, given the billions of dollars and years of planning involved.
He said the levies will drive up costs for businesses, car buyers and workers in Canada and the U.S. “This is not good news for anybody,” Prof. Johnson said by phone. “It’s not good news for Canadian companies and workers. It’s also not good news for the U.S. auto sector.”
The tariffs will cause Canadian job losses in the long term, Prof. Johnson said, but the unsustainable damage they cause in the U.S. will eventually spur their removal. However, Mr. Trump gave no indication that he would back down.
The Trump administration had already imposed a 25-per-cent tariff on Canadian and Mexican goods on March 4, with a lower 10-per-cent levy for energy products, critical minerals and potash. Two days later, he offered a month-long reprieve on tariffs for products that comply with the USMCA. At the time, the President said he offered the break to give automakers time to rejig their supply chains.
On March 12, Mr. Trump imposed 25-per-cent tariffs on steel and aluminum imports, including from Canada.
When asked about the “reciprocal tariffs” that are set to go into effect next week, Mr. Trump said they would be imposed on all countries, but that they would be “very lenient.”
“I think people are going to be surprised. In many cases, it’ll be less than the tariffs they’ve been charging us for decades,” said Mr. Trump.
In retaliation for U.S. levies, Canada has implemented tariffs on some $60-billion worth of U.S. goods.
On the federal election campaign trail, party leaders announced their own plans on Wednesday to protect Canada’s auto manufacturing industry.
Earlier in the day, before the tariffs were announced, Liberal Leader Mark Carney promised that a Liberal government would protect Canada’s auto sector in the face of U.S. tariff threats. He pledged a $2-billion fund to boost competitiveness in the sector, “protect manufacturing jobs, support workers to upskill their expertise in the industry, and build a fortified Canadian supply chain – from raw materials to finished vehicles.”
After the U.S. President’s press conference, Mr. Carney called the latest tariffs a “direct attack” on Canada and Canadian auto workers. He said ties between the two countries are “in the process of being broken” by Mr. Trump. He called a meeting Thursday of the cabinet committee on Canada-U.S. relations.
Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre said Mr. Trump had a history of changing his mind on tariffs. “The message to President Trump should be to knock it off,” he said.
“He should lift these tariffs. But whether or not he does – because he’s changed his mind before, he’s done this twice, puts them on, takes them off, and we can suspect that that may well happen again – we have to become more self reliant and have new and different markets so that we no longer rely on or depend on what is becoming an increasingly undependable customer.”
Mr. Trump has set various tariff deadlines for Canada and Mexico over the past few months, only to change his mind and pause the levies. This has confounded businesses, which rely on certainty when planning their operations.
The Detroit-based automakers have been lobbying against the tariffs, which they said would cause disruption and add billions in expenses. The companies operate plants in Canada and Mexico, and move components across borders several times before a vehicle’s final assembly.
James Farley, Ford Motor’s chief executive officer, warned in February that the tariffs will “blow a hole” in the U.S. industry, leading to “cost and chaos.”
Business and labour leaders expressed outrage at the tariffs.
“These new tariffs on Canada, one of our closest allies and largest trading partners, are unjust and will have lasting negative impacts on American and Canadian workers,” said Brian Bryant, international president of the 600,000-member International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers.
Candace Laing, head of the Canadian Chamber of Commerce, said the tariffs will costs tens of thousands of jobs on both sides of the Canada-U.S. border, driving jobs to other countries.
“This tax hike puts plants and workers at risk for generations, if not forever,” Ms. Laing said. “With this latest tariff, the U.S. administration has committed to taxing America’s automotive manufacturers and increasing the production cost of a car.”